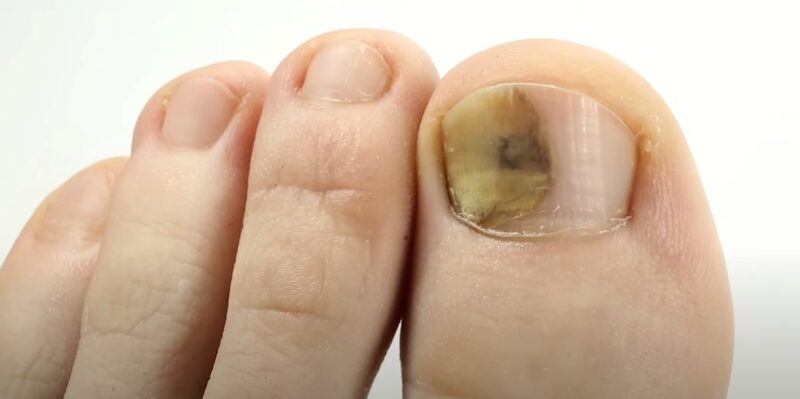
Toenail fungus is a common problem that makes your nails look yellow, thick, and ugly. It can also hurt a lot. There are different ways to treat it, like pills, creams, or natural remedies. The sooner you start, the better chance you have to get rid of it and grow nice nails again. We will introduce you to the most efficient medication to use for this condition.
1. Terbinafine

Terbinafine is an antifungal medication widely prescribed for the treatment of toenail fungus. Its primary function is to eliminate fungal infections by disrupting the fungal cell membrane.
Mechanism of Action
Terbinafine works by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase, which is crucial for the synthesis of ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane. Without ergosterol, the fungal cells become deficient in maintaining their structure, leading to their eventual death and resolution of the infection.
Convenience is one of the main benefits. You can treat the symptoms just like any other condition, such as acne, abdominal pain, or fever.
Indications for Use
This medication is most effective for treating fungal infections of the nail, particularly those caused by dermatophytes. It is suitable for patients looking for a systemic solution to toenail fungus.
Administration Guidelines
Patients are typically advised to take Terbinafine orally once a day for a duration of 6 to 12 weeks. The exact duration depends on the infection’s severity and the individual’s response to treatment.
Potential Side Effects
While Terbinafine is effective, it can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal upset, rash, headaches, and, in rare cases, liver function abnormalities. Regular monitoring and communication with a healthcare provider are essential to manage any adverse reactions.
2. Itraconazole
Itraconazole is another powerful antifungal medication used to treat toenail fungus. It offers a broad spectrum of action against various fungi, making it a versatile choice for fungal nail infections.
Mechanism of Action
Itraconazole functions by binding to fungal cell membrane components, specifically inhibiting the enzyme responsible for ergosterol synthesis. This disruption leads to a weakened fungal cell membrane and ultimately the fungus’s death.
Itraconazole is particularly useful for treating toenail infections caused by yeasts and certain molds.
Indications for Use
Itraconazole is indicated for the treatment of nail fungus infections where the fungus is susceptible to the medication. It is particularly useful for infections that have not responded to other treatments.
Administration Guidelines
The typical course of treatment involves taking Itraconazole in pulse doses, which means taking the medication daily for one week per month, for two to three months. This regimen helps minimize exposure while maintaining effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects
Itraconazole can lead to side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, and congestive heart failure in patients with pre-existing heart conditions. It’s important for individuals to undergo thorough evaluation before starting treatment and to monitor for any adverse effects throughout the course.
3. Fluconazole
Fluconazole serves as an oral antifungal medication frequently used to manage and treat toenail fungus. Recognized for its systemic action, Fluconazole is effective against a wide range of fungal infections, offering an alternative for patients who may not respond to other treatments.
Mechanism of Action
The drug operates by obstructing the fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme, essential for the synthesis of ergosterol, a vital component of the fungal cell membrane. The disruption of ergosterol production leads to cell membrane damage and the eventual death of the fungal cells.
Indications for Use
Fluconazole is particularly suited for patients with toenail fungus caused by yeast and other non-dermatophyte molds. Its use is often considered when other antifungal agents are contraindicated or have proven ineffective.
Administration Guidelines
The administration of Fluconazole for toenail fungus typically involves a weekly oral dose, with the treatment duration extending several months, depending on the infection severity and the clinical response.
Potential Side Effects
Patients may experience side effects such as headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and in rare instances, liver toxicity. Monitoring liver function tests before and during treatment is advisable to mitigate potential risks.
4. Amorolfine
Amorolfine is a topical antifungal medication that offers a targeted approach to treating toenail fungus. Available as a nail lacquer, it provides a convenient option for patients seeking localized treatment methods.
Mechanism of Action
Amorolfine works by inhibiting the biosynthesis of ergosterol, disrupting the fungal cell membrane. Its broad-spectrum antifungal activity is effective against a wide array of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds.
Indications for Use
The medication is indicated for mild to moderate toenail fungus, especially in cases where the infection affects up to two-thirds of the nail or does not involve the lunula (the white area at the base of the nail).
Administration Guidelines
Amorolfine nail lacquer is applied directly to the infected nails, usually once or twice a week. The treatment duration varies, often requiring several months to achieve full nail clearance due to the slow growth rate of toenails.
Potential Side Effects
Being a topical treatment, Amorolfine’s side effects are generally limited to local reactions, such as burning sensation, itching, or redness at the application site. Systemic side effects are rare due to minimal absorption into the bloodstream.
5. Ciclopirox
Ciclopirox is a topical antifungal treatment that comes in the form of a nail lacquer, known commercially as Penlac, among other names. It represents a non-systemic option for patients seeking to address toenail fungus directly through application on the nail.
Mechanism of Action
This medication functions by inhibiting the transport of essential substances into fungal cells, leading to the disruption of fungal cell growth and survival. Ciclopirox exhibits broad-spectrum antifungal activity, effective against a wide range of fungi responsible for nail infections.
Ciclopirox comes in the form of a nail lacquer known as Penlac. It inhibits the transport of essential substances into fungal cells, disrupting their growth and survival.
Indications for Use
Ciclopirox is indicated for mild to moderate toenail fungus, particularly useful for patients preferring topical over oral treatments. It is suitable for infections that do not involve the white area at the base of the nail, known as the lunula.
Administration Guidelines
The recommended application involves painting Ciclopirox nail lacquer on the affected nails once daily, preferably at bedtime, to allow for overnight absorption. The treatment regimen typically extends over several months, mirroring the slow growth rate of toenails and the time required to achieve visible improvement.
Potential Side Effects
Side effects of Ciclopirox are generally localized to the area of application and may include nail discoloration, mild burning, or itching. Unlike systemic treatments, the risk of systemic side effects is minimal due to the limited absorption of the medication.
6. Tea Tree Oil

Tea Tree Oil, derived from the leaves of the Melaleuca alternifolia tree, is celebrated for its natural antiseptic and antifungal properties. It offers an alternative or complementary approach to conventional treatments for toenail fungus, appealing to those seeking natural remedies.
Mechanism of Action
The effectiveness of Tea Tree Oil against toenail fungus is attributed to its compound terpinen-4-ol, which has been shown to kill fungi by penetrating the nail and disrupting fungal cell membranes. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it a versatile option against various fungal pathogens.
Indications for Use
Tea Tree Oil is suitable for individuals with mild to moderate toenail fungus, particularly those interested in natural treatment methods. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments to enhance antifungal efficacy.
Administration Guidelines
For optimal results, Tea Tree Oil should be applied directly to the affected area using a cotton swab or brush, typically two times a day. Careful application ensures the oil reaches the nail bed, maximizing its antifungal action. Consistency and persistence in application are key, as natural remedies may require extended periods to show significant improvements.
Potential Side Effects
While generally considered safe for topical use, Tea Tree Oil can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. It is important to conduct a patch test before full application and to dilute the oil with a carrier oil if sensitivity is a concern.
7. Vinegar Soaks
Vinegar, a common household item, is acclaimed for its antimicrobial properties, making it a popular home remedy for toenail fungus. Acetic acid, the main component of vinegar, is believed to create an environment that inhibits the growth of certain fungi and bacteria.
Mechanism of Action
The antifungal effect of vinegar soaks arises from acetic acid’s ability to alter the pH of the environment, making it less hospitable for fungal growth. This acidic condition is detrimental to many fungal species, potentially slowing down or inhibiting their proliferation on the nails.
Indications for Use
Vinegar soaks are most suited for individuals with mild toenail fungus or those looking for a natural adjunctive treatment to conventional therapies. It’s an accessible option for those who prefer non-pharmaceutical approaches to health care.
Administration Guidelines
To prepare a vinegar soak, mix one part vinegar with two parts warm water. Soak the affected nails for 15 to 20 minutes daily. Consistency is crucial, as the effectiveness of vinegar soaks depends on regular and prolonged use to see noticeable improvements.
Potential Side Effects
Vinegar is generally safe for most individuals; however, prolonged exposure to acidic environments may cause skin irritation or dryness in some cases. It is advisable to moisturize the feet after soaking and to discontinue use if severe irritation occurs.
8. Garlic Extract

Garlic is renowned for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties, attributed to its compound allicin. Garlic extract, either in the form of oil or crushed garlic, is used as a natural remedy for various infections, including toenail fungus.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin, the active component in garlic, possesses potent antifungal properties that can combat fungal pathogens responsible for toenail infections. It works by disrupting the fungal cells’ ability to reproduce, effectively reducing the spread of the fungus.
Indications for Use
Garlic extract is an option for those seeking alternative or supplementary treatments for toenail fungus. Its natural antifungal action makes it suitable for mild to moderate infections, especially for individuals inclined towards holistic health practices.
Administration Guidelines
For topical application, garlic oil can be applied directly to the affected nail with a cotton swab. Alternatively, a paste made from crushed garlic can be applied to the nail and covered with a bandage for several hours or overnight. Treatment should be repeated daily for several weeks or until improvement is observed.
Potential Side Effects
While garlic is natural and safe for topical use, it may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. A patch test is recommended before widespread use. Additionally, the strong odor of garlic is a consideration for those using this remedy regularly.
9. Oregano Oil

Oregano Oil, derived from the leaves and flowers of the oregano plant, is touted for its powerful antifungal and antibacterial properties. Thymol and carvacrol, two of its active compounds, are particularly effective against a variety of fungal infections, including those affecting the toenails.
Mechanism of Action
The efficacy of Oregano Oil against fungal infections is attributed to thymol and carvacrol, which have been shown to disrupt the fungal cell membranes. This action inhibits the growth and reproduction of fungal cells, effectively reducing the spread and severity of the infection.
Indications for Use
Oregano Oil is suitable for individuals seeking a natural, alternative treatment for toenail fungus. It is especially appealing to those who prefer herbal remedies over traditional pharmaceuticals, aiming for a holistic approach to foot health.
Administration Guidelines
Oregano Oil should be diluted with a carrier oil, such as olive or coconut oil, to minimize the risk of irritation. Apply a few drops of the diluted solution to the affected nails twice daily, using a cotton swab or brush. Regular application over several weeks is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Potential Side Effects
Due to its potent nature, Oregano Oil may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. A patch test is advisable before commencing treatment. Discontinue use if severe irritation or discomfort occurs.
FAQs
What happens if you have toenail fungus for too long?
If you have toenail fungus for too long, it can cause pain, difficulty wearing shoes, and permanent damage to your nails. It can also spread to other nails or skin, and increase the risk of bacterial infections.
What happens if you cut off toenail fungus?
Cutting off toenail fungus is not a good idea, as it can make the infection worse and cause bleeding, pain, and injury to your nail bed. You should consult a doctor before attempting any home remedies or self-care for toenail fungus.
Can toenail fungus go away on its own?
Toenail fungus rarely goes away on its own, as it is caused by microscopic organisms that thrive in moist and dark environments. Toenail fungus usually requires treatment with antifungal medications, either oral or topical, or sometimes laser therapy.
What makes toenail fungus worse?
Some factors that can make toenail fungus worse are: wearing tight, sweaty, or wet shoes and socks; sharing personal items like nail clippers or towels; having poor circulation, diabetes, or a weakened immune system; and not seeking medical treatment early.
Summary
Toenail fungus represents a common and challenging condition that affects a significant portion of the population, leading to both cosmetic concerns and potential pain. The condition’s persistence and resilience against simple treatments necessitate a comprehensive approach to management and eradication.
While numerous strategies have been explored to combat this fungal infection, the effectiveness of these methods can vary widely among individuals, influenced by factors such as the severity of the infection, the specific fungal species involved, and the overall health and immune status of the patient.